PUBLICATIONS

Towards a new regulatory model for Healthcare providers
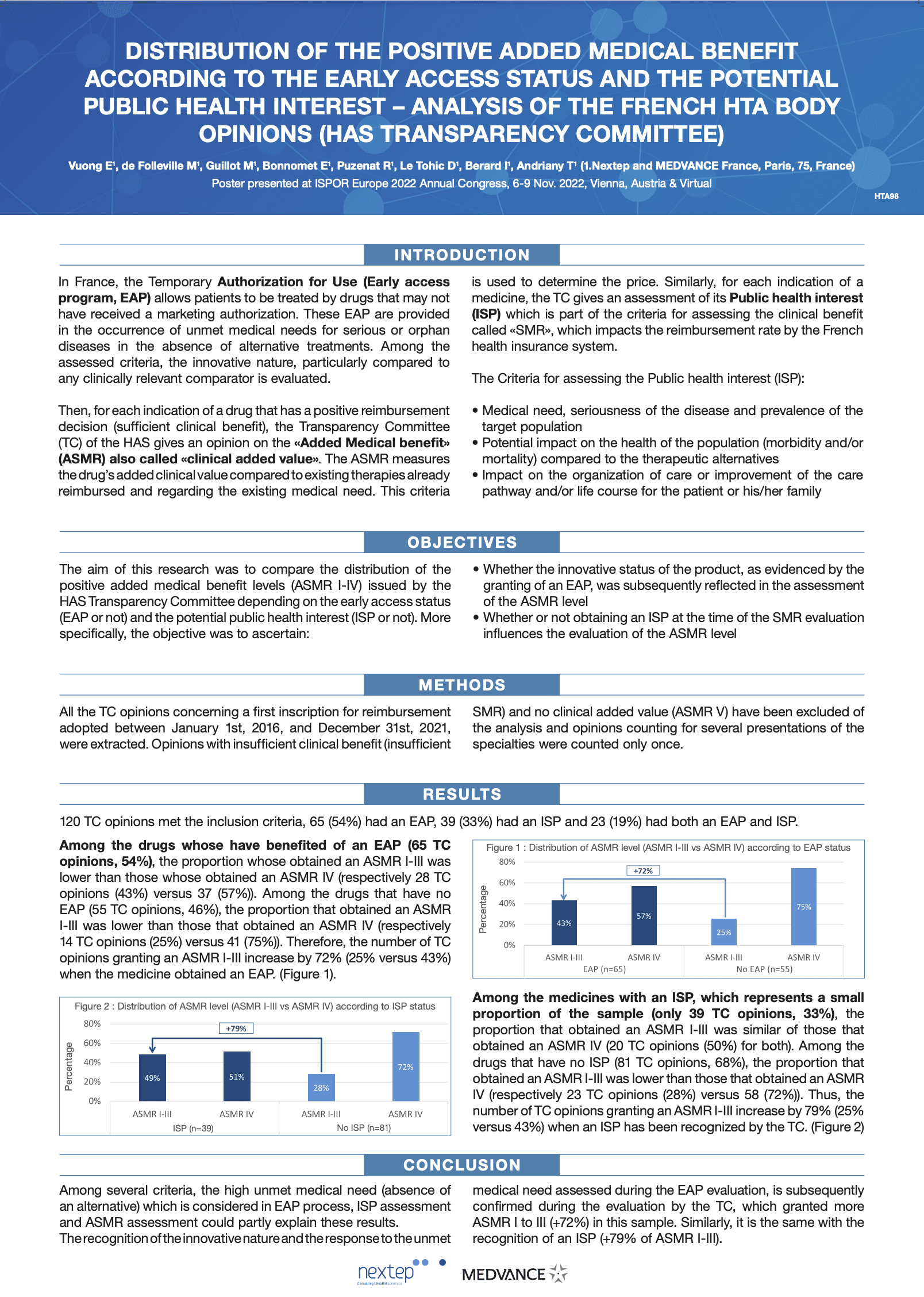
Distribution of the positive added medical benefit according to the early access status and the potential public health interest – analysis of the French HTA body opinions (HAS transparency committee)
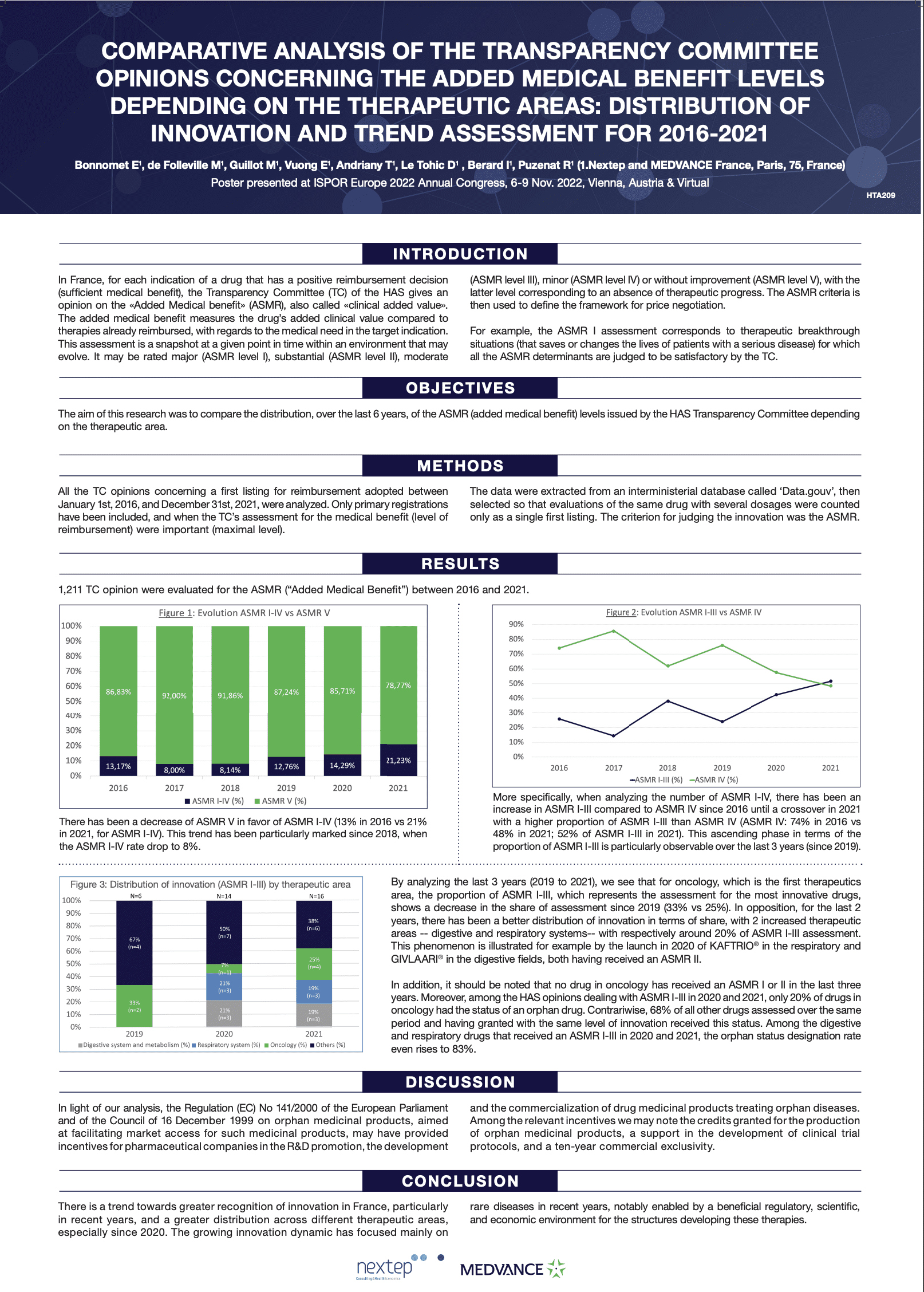
Comparative analysis of the transparency committee opinions concerning the added medical benefit levels depending on the therapeutic areas: distribution of innovation and trend assessment for 2016-2021
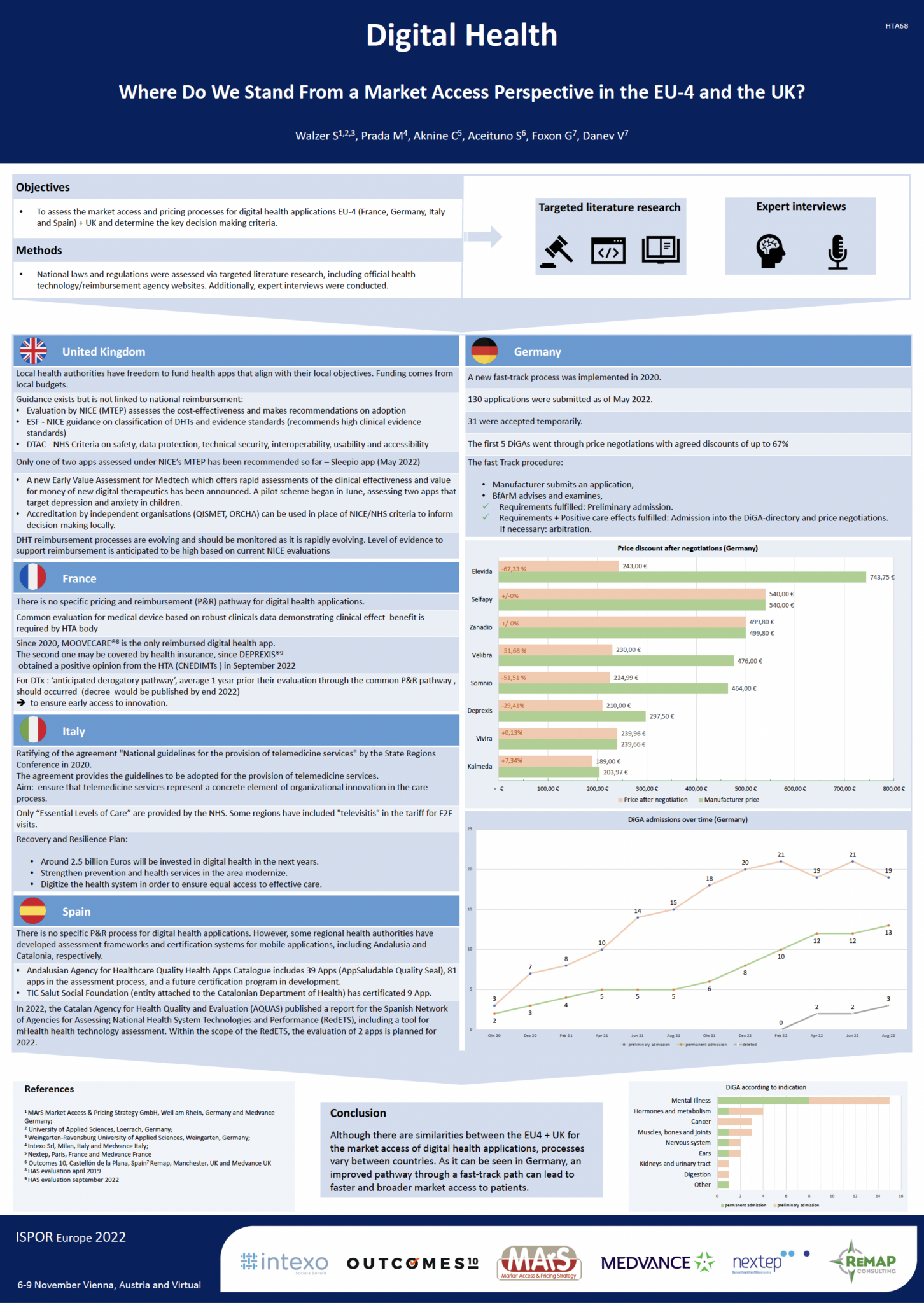
Digital health: Where Do We Stand From a Market Access Perspective in the EU-4 and the UK?
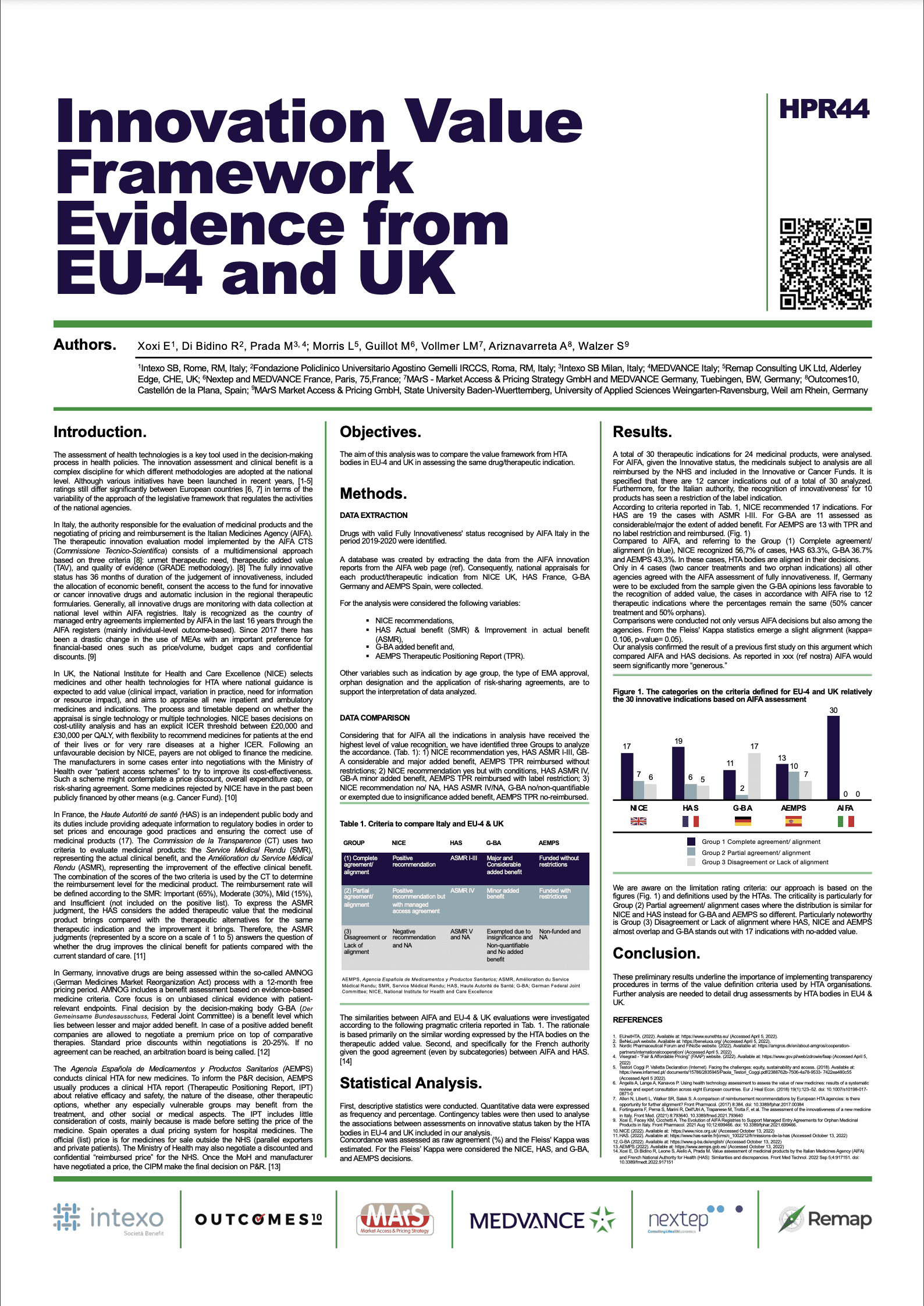
Innovation Value Framework Evidence from EU-4 and UK
Proposals for a healthcare system creating more value for patients.
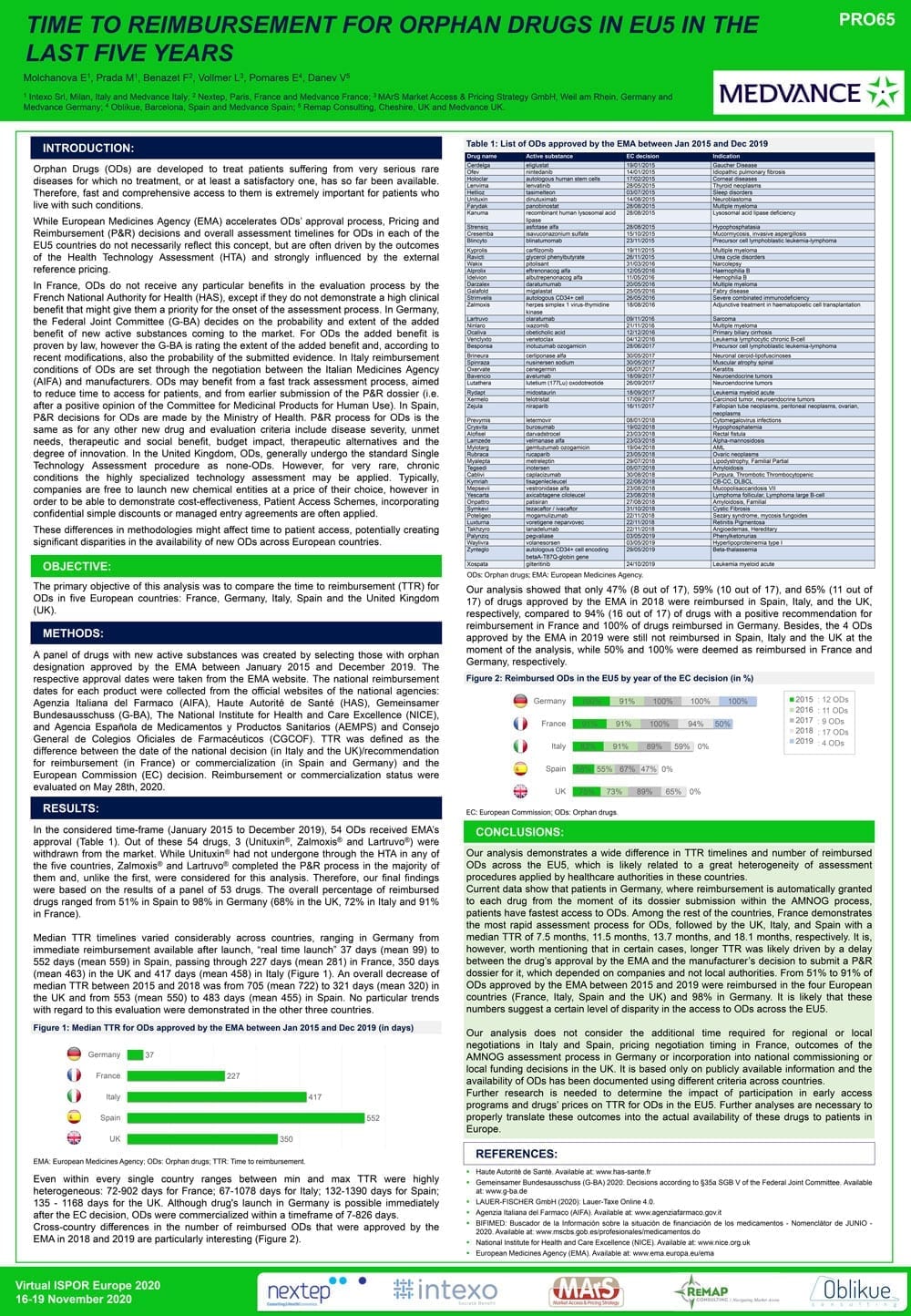
Time to reimbursement for orphan drugs in EU5 in the last five years
Comparison of Market Access Routes of Digital Health Applications in France, Germany and the UK
New digital health applications (DHA) reaching the health care market and some have already proven a clear benefit for patients through RCTs. But how is it with the market access: Different countries handle DHAs similar to other health care products, others have implemented a special pathway. The objective of this analysis is to examine DHA market access routes in Germany, France and the UK.
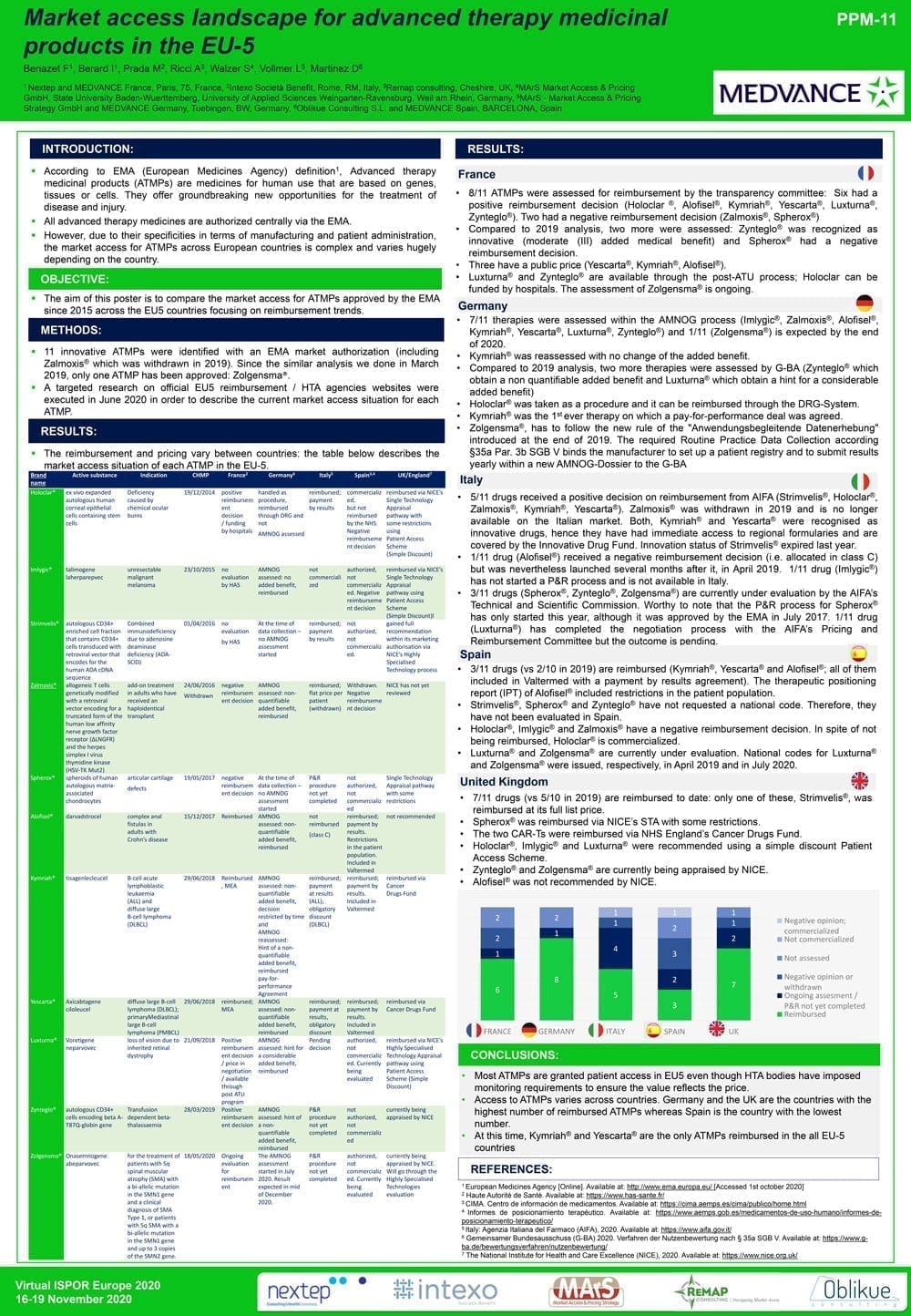
Market access landscape for advanced therapy medicinal products in the EU-5
Innovative gene and cell therapies – market access and reimbursement decisions in the eu5: availability or not, that is the question…
Comparison of early access programs for orphan drugs in the eu-5 countries
There are several mechanisms other than Health Technology Appraisal (HTA) approvals and Pricing & Reimbursement (P&R) decisions by which patients can access orphan drugs pre-launch within a local healthcare system.
Early access programs (EAPs) for orphan drugs differ among the EU member states due to their national regulation based on which the EAPs are implemented.
The objective of this analysis is to examine similarities and differences of EAPs in the EU-5 countries (Germany, France, Italy, Spain and UK).
Market access, pricing and reimbursement processes for orphan drugs in the eu-5 countries: a comparative assessment
The healthcare system in Europe seems simple at first glance. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) centrally regulates the marketing authorization of new medicines in Europe. However, the health systems are not part of the Lisbon Treaty and therefore in the national accountability of the individual European Union (EU) member states. This means 28 different ways of market access and reimbursement.
For orphan drugs, the opportunities of market access begin even before the drug approval through EMA. To show the possibilities, the market access, pricing and reimbursement processes of the big five European countries (EU5) - France, Germany, Italy, Spain and the United Kingdom (UK) - were analysed for similarities and differences.
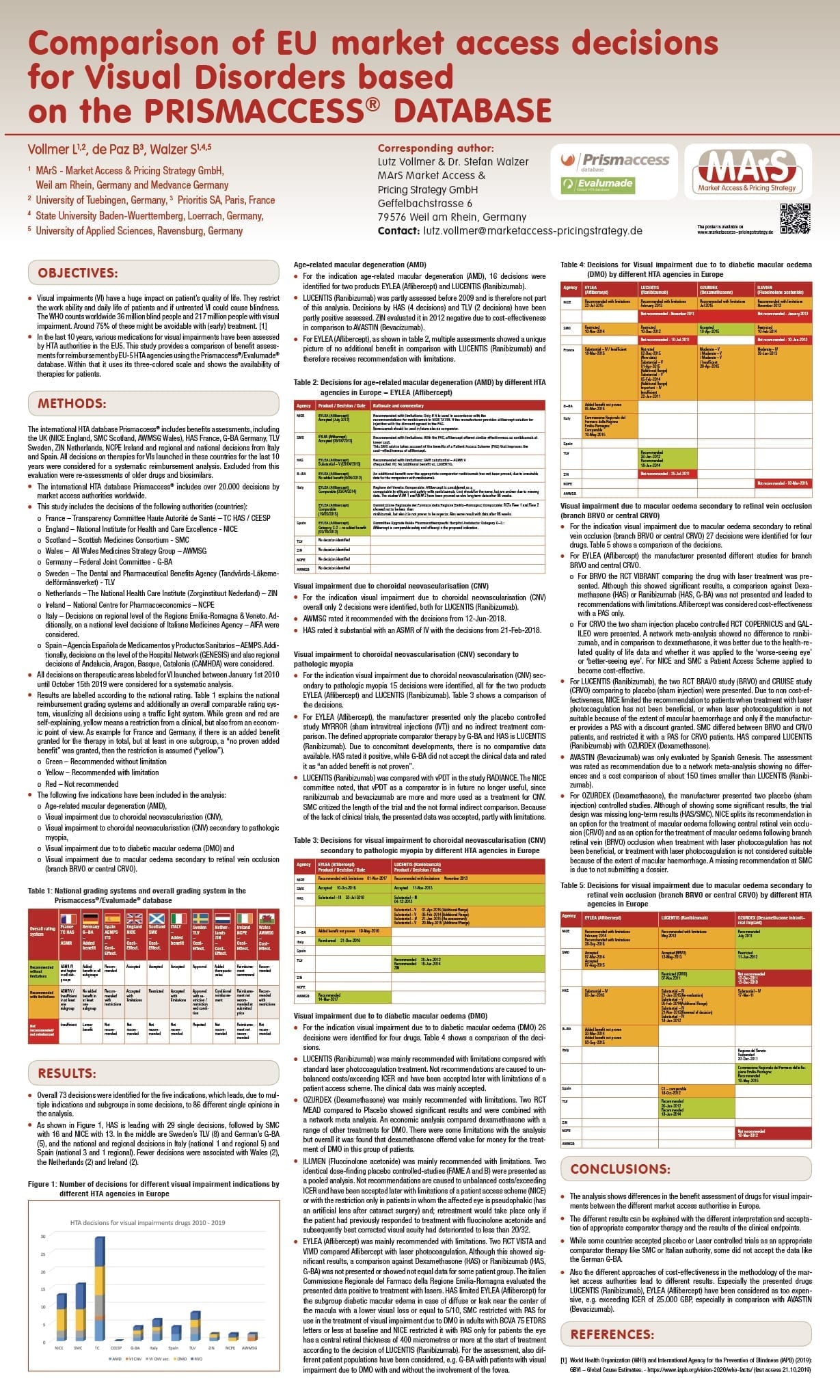
Comparison of EU market access decisions for Visual Disorders based on the PRISMACCESS® DATABASE
Visual impairments (VI) have a huge impact on patient’s quality of life. They restrict the work ability and daily life of patients and if untreated VI could cause blindness.The WHO counts worldwide 36 million blind people and 217 million people with visual impairment. Around 75% of these might be avoidable with (early) treatment. [1]
In the last 10 years, various medications for visual impairments have been assessed by HTA authorities in the EU5. This study provides a comparison of benefit assessments for reimbursement by EU-5 HTA agencies using the Prismaccess®/Evalumade® database. Within that it uses its three-colored scale and shows the availability of therapies for patients.
Hysteroscopic removal of uterine fibroids and infertility treatment: Reimbursement in Germany
Time to reimbursement for orphan drugs in EU5 in the last 3 years
Although the orphan drug designation and marketing authorization (MA) are managed and granted at the European level by the European Medicines Agency (EMA), the pricing and reimbursement process is defined on a national level, is often driven by HTA outcomes and is strongly influenced by the external price referencing.
Pmu57: analysis of the evolution in the access to medicines in italy in the last 5 years (2014-2018)
PRO70: italian law 326/2003 application in the last 6 years: approvals, rejections and economic impact of this early access scheme
PRO76: Italian 648/96 Law application between Jan 2013 and September 2019: focus on orphan drugs
PMU67: Performace-based schemes in Italy: impact of their application in the last 5 years (2013-18)
Reimbursement and pricing times for drugs depending on the early access status in france (with or without an atu)
In France, the Temporary Authorisation for Use (ATU) (early access process) allows patients to be treated by drugs that may not have received a marketing authorisation. These ATUs are provided in the occurrence of unmet medical needs for serious or orphan diseases in the absence of alternative treatments. During this specific early access program, some data may be recorded in order to reinforce the evaluation conducted by the HAS and may impact the P&R delay.
Comparative analysis of the transparency committee opinions concerning the added medical benefit obtained by drugs available through the early access program vs other drugs in france
For each indication of a drug that has a positive reimbursement decision (sufficient medical benefit), the Transparency Committee (TC) of the HAS gives an opinion on the “Added Medical benefit” (ASMR) also called “actual clinical benefit”. The added medical benefit measures the drug’s added clinical value compared to existing therapies already reimbursed and is used to determine the price. In France, the Temporary Authorization for Use (ATU) (early access process) allows patients to be treated by drugs that may not have received a marketing authorization.
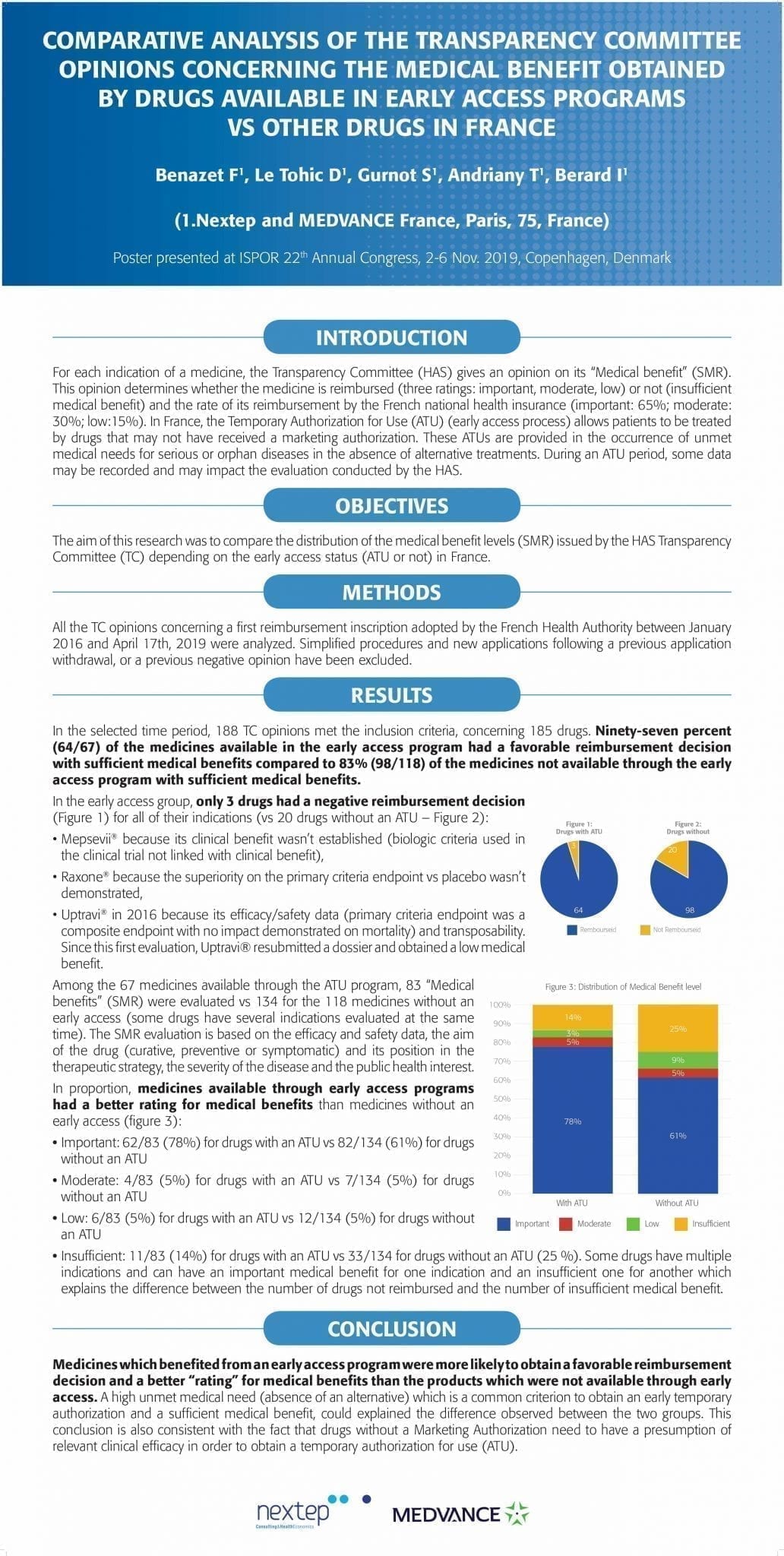
Comparative analysis of the transparency committee opinions concerning the medical benefit obtained by drugs available in early access programs vs other drugs in france
For each indication of a medicine, the Transparency Committee (HAS) gives an opinion on its “Medical benefit” (SMR). This opinion determines whether the medicine is reimbursed (three ratings: important, moderate, low) or not (insufficient medical benefit) and the rate of its reimbursement by the French national health insurance (important: 65%; moderate: 30%; low:15%). In France, the Temporary Authorization for Use (ATU) (early access process) allows patients to be treated by drugs that may not have received a marketing authorization. These ATUs are provided in the occurrence of unmet medical needs for serious or orphan diseases in the absence of alternative treatments. During an ATU period, some data may be recorded and may impact the evaluation conducted by the HAS.
ISPOR 2018
PRICE DIFFERENCES FOR ORPHAN DRUGS ACROSS THE EU-5 COUNTRIES: A COMPARATIVE ASSESSMENT
Pricing and reimbursement decisions after the European marketing authorization are the responsibility of each country, which can lead to inequalities and differences in access and prices for drugs1.
The aim of this study was to assess market access and price differences in the five European Union countries (EU5) for orphan drugs approved by the European Commission (EC)